Environmental, Social and Governance

ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important as investors, stakeholders, and consumers are placing greater emphasis on sustainability and social responsibility. It encompasses a wide range of factors that can impact a company’s long-term performance and reputation. By reporting on their ESG practices and performance, companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainable business practices, improve their transparency and accountability, and enhance their reputation.

Environment
Evaluate how your organization
performs as a steward of
nature

Social
Examine how your organization manages its relationship with employees, suppliers, customers, and the community.

Governance
Management and Compliance
Services
Capacity
Building

GHG
Inventorization

ESG Due Diligence & Risk Assessment

Climate Change Risk Assessment

ESG Reporting and Disclosures

Net Zero & Decarbonization

Sustainability Service Overview
FAQs
- Improves financial performance
- Attracts investors and lenders
- Offers a competitive advantage
- Builds customer loyalty
- Makes company operations sustainable
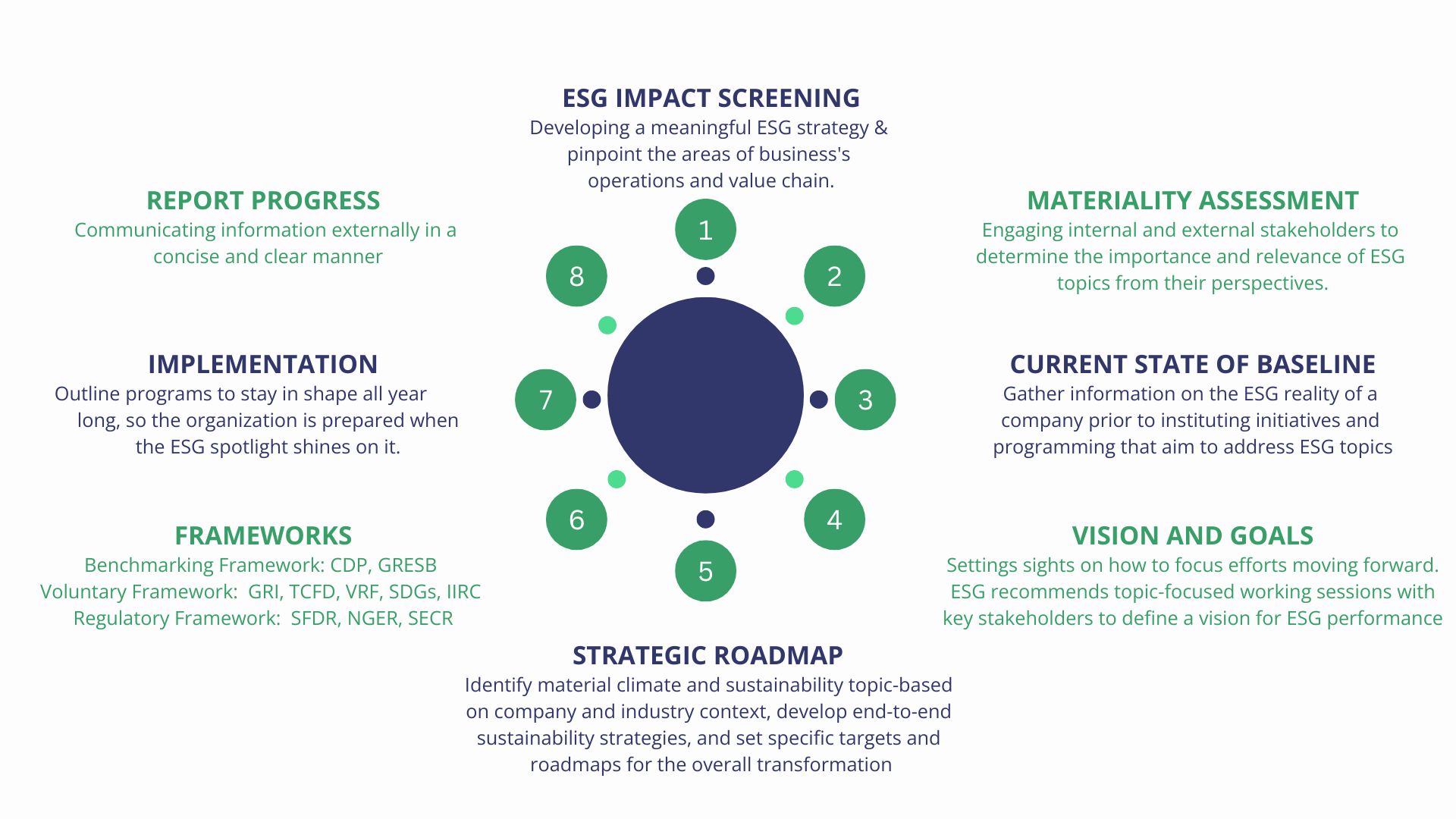
Regulatory Frameworks
Akin to standards, they provide specific topics, methodologies and metrics for companies touse in reporting on their ESG performance.
Example : SFDR, NGER, SECR
Voluntary Frameworks
These provide a platform and mechanisms for ESG disclosures that are applicable to organizations across different industry sectors and regions. Reporting is commonly done through online surveys or questionnaires that are then scored.
Example :GRI, TCFD, VRF, SDGs, IIRC
It is a methodology for assessing the environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a product, process, or service. The stages of a product’s life cycle include:
- Resource extraction
- Manufacturing
- Distribution
- Use
- End-of-life
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR).
BRSR is a mandatory reporting requirement for all listed entities in India. The initiative was introduced by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 2021.
The BRSR framework aims to encourage listed companies to adopt sustainable business practices and disclose information related to their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
The BRSR requires disclosures against the nine principles of the NGRBC. The reporting format is divided into three parts:
- General Disclosures
- Management and Process Disclosures
- NGRBC Principle wise Performance Disclosures
Get in touch!
Anil Kumar V
Head – ESG & Sustainability
esg@kosherclimate.com


